Monday, 12 February 2018
DSNDIST
Ø
Distributed Data Facility – DDF
Ø
Distributed environment provides flexibility to
access data located at different sites.
Ø
Services data requests than come from
DRDA(Distributed relational DB architecture)
Ø
Optional address space – Required when
distributed DB functionality required
Allied
Address space
Ø
Reponsible for handling global lock requests
Ø
Requests to read from group buffer spool
Ø
Available in datasharing environment
DSNDBM1
- Database service address space / ReadIN-writeIN / Physical component
- Database services which is responsible for managing Physical structure of DB.
- Handles SQL related queries
- Core logic of DB2
- Update SYSLGRNX/Interaction with coupling facility
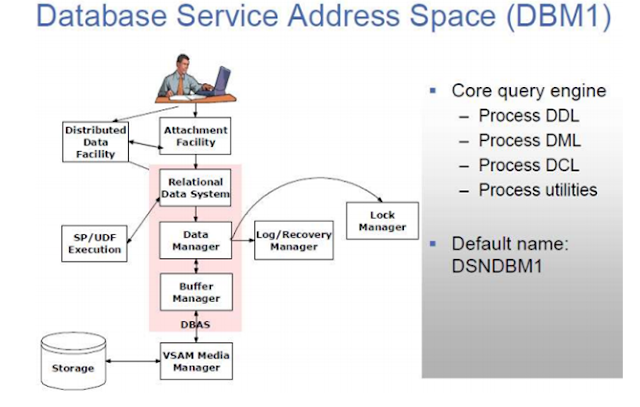
Buffer Spool management
 Relational Data system (RDS)
Relational Data system (RDS) Data Manager (DM)
Data Manager (DM) Buffer Manager (BM)
Buffer Manager (BM)
Relational Data System
o
SQL Compiler (compiles all SQL)
o
Runtime Executor
o
Catalog services
o
Manages Objects
Data Manager
o
DB2 Engine
o
Makes requests to get/create/alter data
o
Invokes buffer manager
o
Interface with IRLM
Buffer Manager
o
Access Physical data for data manager / Index
Manager
o
Searches for page in Buffer spool , if there is
no page then VSAM media manager to return from DASD
DSNMSTR
SYSTEM Service component/ System service address space /
Thread Factory
Ø
Controls connection to other MVS subsystem
Ø
Handles/Initiates system startup and shutdown
Ø
Handles Operator communication
Ø
Manages system Log and archiving logs
Ø
Thread Creation /termination (Thread factory)
Ø
Manages DSNZPARM
Ø
Initial level authority
Ø
Supports recovery management
Sunday, 11 February 2018
Version - chronology
Here we see each version/release of DB2 in its thirty year
history, along with its date of general availability. The other two columns,
EoM and EoS, are end-of-marketing and end-of-service dates. An EoM date means
that IBM will no longer sell that version of DB2 as of that date; EoS means
that IBM will no longer officially support that version of DB2 as of that
date.
Version
|
GA
|
EoM
|
EoS
|
SKIP
|
Code
|
|
1.1
|
1985-04-02
|
No Skip Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
1.2
|
1986-03-07
|
No Skip Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
1.3
|
1987-06-26
|
No Skip Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
2.1
|
1988-09-23
|
No Skip Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
2.2
|
1989-09-22
|
No Skip Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
2.3
|
1991-10-25
|
No Skip Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
3
|
1993-12-17
|
1999-11-30
|
SKIP Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
||
4
|
1995-10-30
|
2000-12-01
|
SKIP Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
||
5
|
1997-06-27
|
2001-12-31
|
2002-12-31
|
SKIP Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|
6
|
1999-06-15
|
2002-06-30
|
2005-06-30
|
SKIP Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|
7
|
2001-03-30
|
2007-03-05
|
2008-03-30
|
SKIP Level
|
ASCII/EBCID
|
|
8
|
2004-03-26
|
2009-09-08
|
2012-04-30
|
SKIP Level
Mode level
|
UNICODE/ASCII/EBCID
|
|
9
|
2007-03-06
|
2012-12-10
|
2014-06-27
|
SKIP Level
Mode level
|
UNICODE/ASCII/EBCID
|
|
10
|
2010-10-22
|
2015-07-06
|
2017-09-30
|
SKIP Level
Mode level
|
UNICODE/ASCII/EBCID
|
|
11
|
2013-10-25
|
SKIP Level
Mode level
|
UNICODE/ASCII/EBCID
|
|||
12
|
No
SKIP / No Mode
|
UNICODE/ASCII/EBCID
|
||||
From
DB2 V8 unicode has been introduced to avoid ASCII/EBCID . Also Mode level in
upgradation introduced.
CM - Compatabilty
Mode
ENFM - Enable
new function mode
NFM - New
Function Mode
DB2V9
catmaint can run on ENFM .We can fall back from ENFM to CM
V10
-> V11 –> V12 allowed
V10
-> V12 Not allowed
Saturday, 10 February 2018
DB2-An Overview
DB2 is a database
product from IBM.DB2
for z/OS is a relational database management system
that runs on the mainframe. It is a Relational
Database Management System (RDBMS). DB2 is designed to store, analyze and
retrieve the data efficiently.
A relational database is
a database in which all of the data is logically contained in tables. These
databases are organized according to the relational model. In a relational
database, referential integrity ensures data integrity by enforcing rules with
referential constraints, check constraints, and
triggers.
Evolution of DB2
In
1983, DB2 for MVS Version 1 was born. “DB2” was used toindicate a shift from hierarchical
databases—such as the Information Management System(IMS) popular at the
time—to the new relational databases. DB2 development continued onmainframe
platforms as well as on distributed platforms
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)












